Article Navigation
I will start with a short story related to 5G network. Do you think it could be real in a couple of years?
“This looks good, John. Great work, and here’s for another successful month”, you say with a smile and close the report with a wave of your hand in the air. You look for your briefcase, but you cannot see it anywhere around you. It’s an old habit. An old habit from different times. Nowadays, almost everything exists in a world of ones and zeroes – it is online, in the cloud, in VR (virtual reality), in AR (augmented reality) …
John is still on the other side of the screen. You catch a glimpse of him turning his head around. He is probably also looking for his briefcase. You smile again. “Goodnight, John”. The screen goes black for a second, and then it changes to a news feed. You sit in the front seat of your car. Alone. “Car, turn off the ambient lights”. The interior goes dark. The dying light of the sun is not enough to bother you.
“Sir, you’ll be home after exactly one hour”, the voice of the car sounds so real. You feel like saying “Thank you”, but you know that there is no point in being polite. It is just a machine. You say it anyway.
You close your eyes.
It’s time for a little nap.
You are alone. The car keeps on its course. It’s fully autonomous, and you trust it.
Is this the future? Yes! And it’s closer than you think – if you thought that it could be real – you are perfectly right. We just need one important component – the 5G network. The last generation of mobile networks that will disrupt everything – our lives, work, business, and even whole industries.
Not just a story. This is what you will learn from this article:
- The state of 5G network.
- Myth or reality: is 5G dangerous to our health?
- Is 5G pose any security dangers?
- How will 5G transform Healthcare?
- How will 5G transform Logistics and Manufacturing?
- How will 5G transform Application and Software Development?
- Should you adopt the 5G network right now? Will it change your business?
5G Network: All the promises in the world
Maybe you had enough of the connected homes and car scenarios. I know that I had my fair share. But the thing is that they describe so well how our lives and industries will change. Because think about it – every single element from the story is possible. It’s not far-fetched science fiction.
Two years ago, at the beginning of September 2017, Renault introduced their concept for a self-driving car – Symbioz. Two months later, journalists from all around the world had the chance to test it on a highway near Paris. Two years ago.
Currently, Renault is testing autonomous shared car service in Paris-Saclay “urban campus” in France. Roughly 100 people will be part of the test. Also, the French automaker, in partnership with (a company that develops technology for self-driving cars), proposed a plan to connect Roissy-Charles de Gaulle Airport and the business district of La Defense with autonomous mobility service.
The technology for autonomous vehicles is developing crazy fast. The biggest uncertainty here is if the regulations can be fast and agile enough to catch up with technology. The second one is when we will have a stable 5G network that can support all the M2M (Machine to Machine) and H2M (Human to Machines) communications.
What about the mixed reality – the merge of the real-world with virtual elements? Today, there are a lot of mixed reality headsets that can combine the real environment around us with virtual elements. Just like Microsoft’s HoloLens.
The intelligent voice assistants? We even have them on our phones and in our houses through smart speakers like Google Home and Alexa Echo! Well, they still cannot make decisions on their own (like JARVIS from Iron Man), but Google Assistant can call your favorite restaurant and make a reservation on your behalf. And the person on the other side may not even know that is talking to a virtual assistant and not a human (Google added a message that is informing the person on the phone, but it did it only after the negative feedback of its absence).
According to Kenneth Research, the Smart Home Industry will reach 124.57 billion USD by the year 2025.
As you can see, all the futuristic parts from the opening part are real. Now imagine all the companies and the technologies behind them. And the only thing that is missing is the connection – the 5G network that will connect everything around us.
That is precisely why the 5G technology has such a divisive image in society and the business. We have the big promises of technology and how it will completely change our lives, and at the same time, it’s a new technology that gives birth to a lot of myths.

In 2019, the first real steps toward the implementation of the 5G networks let to the first misconceptions that went viral, planting the seed of fear in the users’ minds. The business has its doubts as well – would this investment be worth it and what benefits it will bring?
Are all the dangers of 5G myth or reality?
What is 5G Network?
Every new generation of mobile networks has its specifics and every new G (It’s all about the Gs, right?) made a difference to the society and the business.
Mobile networks. The overview:
- 0G Network – Zero generation was a pre-cellular era network that was available as a commercial service. The users had to use big communication devices that were usually installed in cars or were in the form of a hefty briefcase.
- 1G Network – This network supported only an analog voice and the calls were made through big chunky mobile phones. But it was a new way for the users to communicate even if they were far from their home or office. The 1G network gave us stable communication on the move. The start of the first commercial network was in Japan in 1979 and two years later – in Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Sweden.
- 2G Network – The launch of the second-generation mobile network was in 1991. It made the jump from analog to digital. The 2G network added the possibility for the users to connect to the internet through GPRS (2.5G) and EDGE (2.75G) technologies. The second generation brought encryption, more efficient use of the radio specter, SMS text messages, and on the later stage – internet connection.
- 3G Network – The era of mobile applications! The dawn of smartphones, the boom of the mobile internet and the moment the mobile phone becomes something more – a computing device for work, leisure time, navigation. The first commercial 3G networks were introduced in 2001.
- 4G Network – This is the era of the smartphone. The fourth generation is a faster network with much lower latency (the time it takes for a bit of data to travel across the network). 4G opened the door to entirely new services, software, apps, and it transformed industries. Because of this network, we can stream audio and video with high quality, we have social media and services like Uber and Airbnb. The latency with 3G was 135ms and it dropped to 75ms with the introduction of the fourth generation. The latency of the 5G is expected to be as low as 1ms.
- 5G Network – The network that is expected to change everything. The broadband connection of this network means that it will be able to send and receive a huge amount of data without latency, and the speed will reach around 10 gigabits per second (600 times faster than the average 4G speeds). This means a constant and stable connection between people (P2P), people and machines (P2M), and machine to machine (M2M). This will revolutionize different industries, including logistics, healthcare, manufacturing, entertainment (movies, gaming). Adding more and more connected devices is just opening more and more opportunities for the business.
The 5G network: What frequency it will use?
This 5G network uses the millimeter wave (mmWave) technology, which is situated in the very high end of the wireless spectrum. There is a lot of unused bandwidth but there is a catch – the waves are less reliable over long distances and can be easily disrupted – by walls, trees, and even rain.
In the USA, for example, the FCC (Federal Communications Commission) is pushing for more spectrum so 5G is expected to use some of the frequency bands that were used by the previous generations of wireless networks – low-band 600MHz, mid-band in the 2.5GHz, 3.5GHz, and 3.7GHz-4.2GHz bands. The FCC has already auctioned off airwaves in the high-bands – 24GHz and 28GHz, and later this year, it’ll auction off-licenses in the 37GHz, 39GHz, and 47GHz bands. Those are the said millimeter waves.
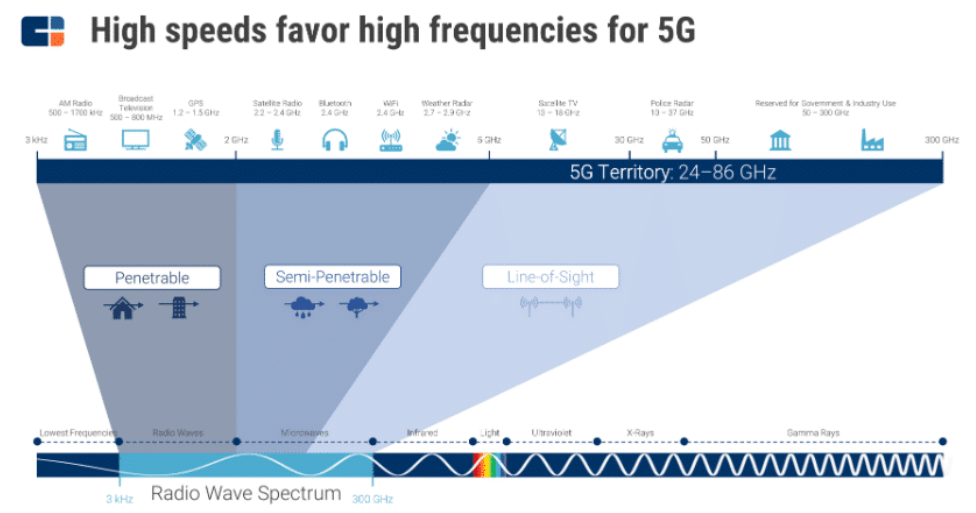
And because they are so unstable and with short scope, the carriers will need to deploy huge numbers of small access points in cities, instead of relying on a few big cell towers as they do today for the 4G network. The millimeter-wave access points could be as small as a smoke detector and they will be virtually everywhere. This way the carriers and the business can be sure that they have solid coverage for all of the connected devices around us.
Is the 5G network dangerous for our health?
Birds are falling from the sky. Radiation is attacking us from everywhere. It’s a matter of time for our health to suffer the irreversible consequences that will lead to the end of humanity.
An apocalyptic scenario, right? These are the consequences of the 5G network adoption according to some of the most shared and comments web pages. Pages that are full of conspiracies. They are insisting on how dangerous the 5G network is. But is it, or it is just a myth, that started from misinformation? Well, yes and no.
Let me explain.
As above mentioned, the biggest concern is the high-frequency radio waves (mmWave). The 5G network will operate near the highest frequencies. Lower down are the wireless networks that our current smartphones use, as well as the wireless connection at our homes, and offices. The millimeter-wave spectrum has never been used for telecommunications. The reason is not because of the unknown dangers but rather the impracticality – it is not that effective at long distances. Or if there are any obstacles along the way, such as buildings, trees, and even people.
Before we continue, check this diagram from Wikipedia:
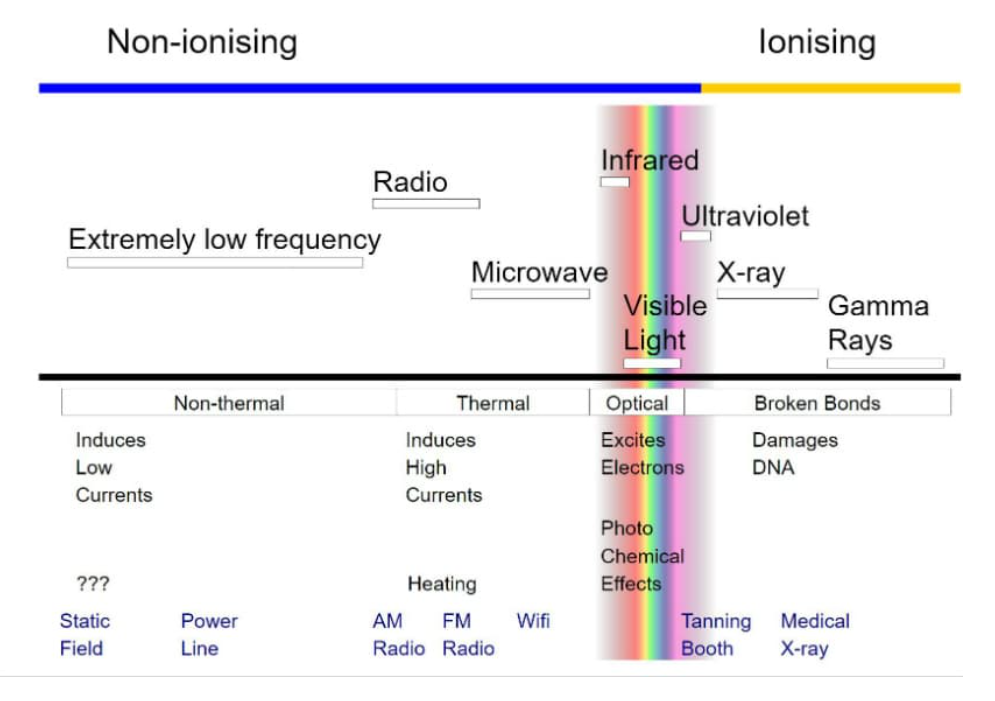
It clearly shows the difference between the two types of radiation – ionizing and non-ionizing. The first one includes gamma-rays, UV rays from the sun and X-rays. They are dangerous to our health because they can penetrate the human body and break apart its atoms.
Every single communication frequency used until now, including the spectrum for mmWave that the 5G network will use the most, is in the non-ionizing part of the spectrum.
So, what is the problem then? The lack of consensus. The thing is that according to some reports and tests, the radio-frequency waves like the kind that emanates from cell phones are drastically raising the risk of cancer. One of these reports is made by the National Toxicology Program (NTP) and is based on their research in which a group of rats was exposed to RF (radio frequency) and they developed malignant tumors. Well, this is the part that all of the anti-5G groups are talking about.
“Exposures used in the studies cannot be compared directly to the exposure that humans experience when using a cellphone,” according to John Bucher, a senior scientist for the NTP. And the most peculiar thing is that according to the research the male rats that were exposed to RF had an increased life span than the rats in the control group. This is somehow left behind in the anti-5G articles. It is not that the RF waves can expand your life, but it is an example of how unsure the results are and that we need more results, based on real-life usage.
“In this age where myths perpetuate rapidly, it is increasingly difficult to differentiate fact from fiction, but it’s crucial we hone our critical thinking and scientific skepticism rather than succumb to groundless falsehoods. Our collective well-being depends on it.”
David Robert Grimes | Cancer researcher, physicist, and John Maddox Prize-winning science writer
The World Health Organization (WHO) categorizes RF waves from mobile phones as a possible carcinogen. Dangerous, right? Well, if you just let me list some of the other things in that category – acrylamide (an ingredient in the coffee), red meat, and so on.
In one of the most recent reports on the topic, Scientific American published an opinion piece with the headline “We have no reason to believe 5G is safe”. Here is a sample statement:
“Millimeter waves are mostly absorbed within a few millimeters of human skin and in the surface layers of the cornea. Short-term exposure can have adverse physiological effects on the peripheral nervous system, the immune system, and the cardiovascular system. The research suggests that long-term exposure may pose health risks to the skin (e.g., melanoma), the eyes (e.g., ocular melanoma) and the testes (e.g., sterility).”
Less than two weeks later, Scientific American published a new opinion piece. Its headline is “Don’t fall prey to scaremongering about 5G” and in it, the author argues that the previous text is based on “fringe and fatally flawed conjecture, attempting to circumvent scientific consensus with scaremongering”. Apart from the NTP study, there are the now-debunked findings of a study of radio waves effect on brain tissue and how dangerous are they for our health. The problem is that the author, physicist Bill Curry, neglected to take into account that our skin protects the inner tissue from the high-frequency radio waves.
The conclusion of the World Health Organization is that “A large number of studies have been performed over the last two decades to assess whether mobile phones pose a potential health risk. To date, no adverse health effects have been established as being caused by mobile phone use.”
The logical question is that if the 5G network is completely safe, then why are some local governments put on hold its development? Part of the problem is the installation of all the small cell sites, other is all the health uncertainties because of the lack of consensus.
In a nutshell, is the 5G network dangerous for our health? Most likely not, but the scientists must continue with their tests – just like their doing with coffee, red meat, alcohol, sun rays, etc.
Is the 5G network pose a security danger?
The next “myth or reality” question is absolutely valid. Everything that surrounds us will be connected – our homes, pets, cars, even our clothes. This will result in a lot more points for possible attacks and a lot more sensitive data that can be stolen. The users could end up being in constant fear of malicious attacks or of being constantly under surveillance.
The presumption is that the more devices are connected, the more opportunities for breach there would be. Besides, in the network, there will be things like cars, airplanes, drones, military equipment, that can be possibly dangerous to our lives if breached by hackers. It’s a completely new type of threat that we haven’t dealt with before.
In 2015 a Wired investigation proved that hackers could breach the security systems of a car, which gave them almost full control over the vehicle. After that, they could easily make the car crash. This was almost five years ago.
What is the situation now?
One of the most commented topics is the situation with Huawei. The Chinese manufacturer of consumer electronics (the second-largest smartphone company in terms of shipments) and the biggest telecommunication equipment provider was blacklisted by the USA President because of suspicions for working with the Chinese government. According to the USA government, this means that Huawei, the company that has the most advanced 5G technology that is even cheaper compared to one of its competitors, can be a Trojan horse for its local government.
Currently, Huawei is banned from the USA with the FCC (Federal Communications Commission) saying that it’ll cut off funding to wireless carriers if they are using equipment from Huawei or ZTE, another Chinese company working in the segment. The UK government is still delaying the decision if they will continue to work with Huawei or not, Norway won’t ban the company. But banning Huawei hardware will not secure those networks. Even in the absence of Huawei equipment, systems still may rely on hardware developed in China, and software can be reprogrammed remotely by malicious actors.
Besides, one of the biggest advantages of the 5G network could be a useful tool for malicious attacks – its speed. Distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks will likely increase, as 5G will boost IoT’s participation in real-time enterprise systems. And IoT is built on the old client/server model, with old security mechanisms. This will take time to adaptively correct.
In a joint statement, the European Union Member States identifies a number of possible security challenges with the mass adoption of the 5G network.
Some of the points include:
- Increased risk of attacks and more potential entry points.
With the increasing role of the software increases the risk of security flaws. The poor software could mean an easier way for hackers to breach the system. Also, every connected device could be dangerous for the system because of malicious backdoors. Therefore, it will be of great importance for the business to use only trustworthy software and service partners. Partners like ScaleFocus.
- Increased risks from major dependencies on suppliers.
A major dependence on a single supplier increases the exposure to a potential supply interruption, resulting for instance from a commercial failure, and its consequences.
- The integrity of the network itself.
With so many connected devices, machines, and services, the 5G network will be the most important part of the system. If there is a problem with the network, this could lead to unexpected outcomes.

How secure is the 5G network?
The carriers and suppliers understand how important is to secure the equipment and the devices in the 5G network from the start, protecting personal data and business-sensitive information. Governments, telecoms, and hardware manufacturers are working to secure the 5G network and their devices. AT&T, for example, has created a special cybersecurity unit that is focused on IoT. All the sides of the 5G adoption know that they must convince the business and the users that the network is secure to succeed with its adoption. The network must have cross-layer security, end-to-end security, and cross-domain security.
According to Andy Purdy, former director of national cybersecurity at the U.S. Department of Homeland Security, there is no reason to think the 5G network is inherently more vulnerable, or riskier, than the previous generation of mobile technology. He argues that the new generation is taking all the experience and all the security directives that we learned and developed for the 4G network and is even adding new security protocols. For example, 5G technology provides better roaming encryption – 256-bit compared to the 128-bit standard used by 4G.
All of these mean that the role of the security companies and the security providers and consultants will be bigger. And we are ready for that.
How will 5G network transform Healthcare?
In a lot of ways! This is one of the industries that will be most influenced by the fifth G. And this is a great opportunity for the business.
In a nutshell, healthcare will benefit from:
- Increasing consumers’ attention to wellbeing.
- Increasing cost to fit with social demographic changes.
- Increasing demand for quality, patient safety, and data storage.
- Changing consumer behavior, freedom of choice and alternative service providers.
All of these will lead to even higher adoption of connected devices, increasing the need for well-developed software and applications for them. Hence, opening new opportunities for hardware manufacturers, insurance companies, and Telecoms.
In China, they have already performed the first surgery over a 5G network. The doctor was controlling surgical instruments from 3000 km. Just imagine how this will change healthcare for so many people that currently don’t have easy access to vital services and surgeries.
5G can bring healthcare to everyone’s home. With the help of IoT devices, doctors can monitor their patients all the time and be aware of their health condition. At ScaleFocus we even have a working model for multimodal coaching cloud-based platforms for supporting older people.
5G network and all the connected and wearable devices will be collecting data all the time. Data will be analyzed and will help for a better understanding of the human body, diseases, treatments, etc. All the data can be used for training AI to detect and thus prevent fatal outcomes. The doctors will make well-informed decisions even before the first symptoms. Their actions will be proactive, rather than reactive, thus saving a lot of lives.
“Data is fundamentally changing the research enterprise and creating new extraordinary opportunities to learn things that were either un-learnable or would have taken generations.”
Harnessing the Power of Data in Health | Stanford Medicine 2017 Health Trends Report
How will 5G network transform Logistics and Manufacturing?
The answer is short – with optimizations, based on automation and data analysis. Just like with healthcare, Big Data will be a key part of the transformation of the manufacturing industry. All the data that is collected and analyzed will help for the establishment of new optimal processes.
The benefits for manufacturing:
- Hyper competition with no sustainable competitive advantages.
- Increasing volatility from business cycles and product life cycles.
- Smart factories advancing from software development in the IoT and automation.
- The optimized logistic means faster processing of inquiries, autonomous warehouse vehicles, etc.
Today, robots are a big part of the manufacturing process. With the introduction of the 5G network, they will become even more useful and skillful in their work because of the data and lightning-fast connection, without the need for a cable. Before the 5G network, this was not possible because the latency had to be as minimal as possible.
“We’ve gone from a stage of imagining, ‘Could 5G be real?’ To really find ourselves in a place where we’re seeing 5G not just in our labs. We took it out of the labs and actually put it into production.”
Tami Erwin | Verizon Business Group | CEO
This quote is from an interview for CNN and was made in the context of the partnership between Verizon and industrial manufacturer Corning. The goal of the partnership is to show in real life how the “fifth G” will change the manufacturing process in one of the biggest facilities of Corning. The company specializes in hardening glass, ceramics, and related technologies. You may know it as the manufacturer of the protective glass over the screen of your smartphone.
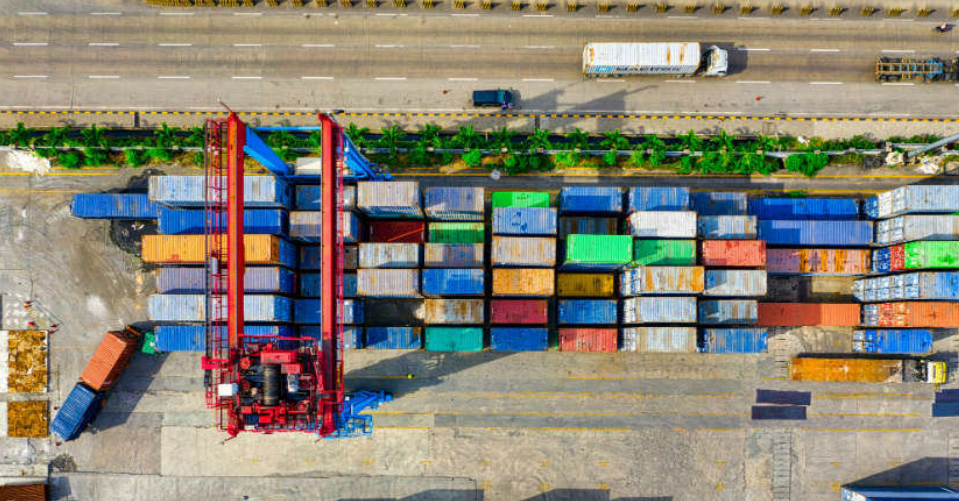

5G will help the manufactures manage better their products and make their logistics process safer, optimized, and cheaper.
The partnership will show if there are any imperfections and unknowns with this process and how will the heavy machinery work with the new wireless connection. According to Claudio Mazzalli, Vice President of Corning, the partnership will show if it is possible to replace the humans driving materials around the plant with self-driving cars, for example. The idea is that with the fast, stable wireless connection with 1ms latency the self-driving cars will move around quickly with the materials. They will constantly know in what speed they can move with, where to turn to save energy and time. This will help Corning save costs and optimize their processes.
Of course, for all of this to work, the factory was equipped with enough 5G network adapters. The other big question is security. The automated collection of so much data must be protected. According to Mazzalli, 5G technology will make their system even more secure. As a part of this partnership, this is a logical answer but it’s not without argument. Today, all the machines are connected to the company’s servers through a cable or WiFi. With the 5G everything goes through a single network. This gives a higher level of control.
How will 5G transform Application and Software Development?
All the benefits that the 5G network brings will have an impact on the way we use applications and the way they are created.
Just a reminder – this is how 5G compares to 4G:
- 10x reduced connection density.
- 10x reduced latency (as low as 1ms).
- 100x more traffic capacity.
- 100x network efficiency.
Currently, the average American spends over two and a half hours per day on mobile apps. The time the user spends on the internet, not through the app? Under half an hour. About 60% of all mobile traffic at the end of 2018 was for video streaming. Most of it – with low quality. This will change and the predictions are that around 74% of all traffic will be video by 2024.
5G technology translates to a revolution in machine learning, artificial intelligence (AI), VR (virtual reality), AR (augmented reality), and the Internet of Things (IoT). This means that it can leverage a lot of data, thus opening the door for a new approach to software development. Just like 4G opened the door for services like Uber, Spotify, Netflix, etc.
With the introduction of the 5G network, the way the users consume information and the way they interact with it will fundamentally change. This will finally leverage the promises of virtual and augmented reality. Users will no longer stream just a video and music but will be able to interact with virtual worlds via their mobile devices. At the same time, the speed of the 5G network opens doors for the streaming of high-quality games. The hardware will step back and the software will be the most valuable requirement. Well, the software and the 5G network.
5G network: Benefits for software development
- 5G technology will let the developers deploy code securely, reliably, and quickly.
- Speed and latency constraints will stop being a problem which will allow us to add new functionalities to our applications faster.
- 5G will have an enormous impact on software development related to augmented reality and 3D gaming.
- The new broadband connection will lead to new mobile applications for unexpected new user-case scenarios.
- The 5G network will be able to accommodate a huge number of users at the same time.
- The wide-spread adoption of VR and AR technologies will create opportunities for never-before-seen services, like training programs in the virtual or augmented world.
- The hardware limitations will no longer be a factor for the development of the software. All the computing will be happening in the cloud. Therefore, developers will create more powerful applications and services.
Throw IoT in all of this, and it’s clear how 5G technology will change the way we create, think of and use applications.
We are prepared for that all-connected world. Applications, solutions based on AI, blockchain – we’ve got you covered.

Should you adopt the 5G now?
This is the billion-dollar question, right? And the thing is that there are a lot of benefits to the 5G network, but there is one big drawback – it would take time and a lot of investments. Just like any other technology of such promise.
Let me give you an example with some digits from the carriers in the USA. Verizon is spending $17 billion annually in capital expenses to roll out 5G. For AT&T the investment is around $20 billion, according to S&P Global Market Intelligence data.
The higher radio-frequency means a lot more base stations and, therefore, a bigger investment.
And the results may not be as quick as the business would like them to be. Maybe, this is the reason for the results from an Accenture survey. It was conducted among 1800 executives from mid-sized and large businesses. The answers showed that more than half of them “don’t expect that the technology [5G network] will enable them to do much that they can’t already do”. But that is not all.
Throughout December 2018 and January 2019 Tech Pro Research, a ZDNet’s sister site surveyed 164 professionals what is their attitude towards the new technology. 85% of the respondents are already using 5G technology or have plans to adopt it in the future. It will be naive to think that the surprising enthusiasm will transfer into 5G deployment, but it’s an interesting statistic. Especially, when 56% of the surveyed professionals believe that 5G will enable new technology that they could not use before.
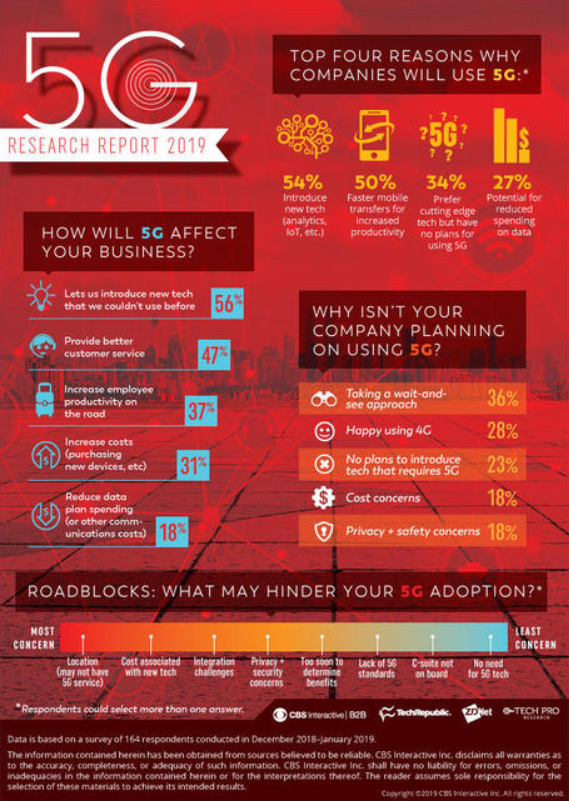
What does the business think about 5G?
The business finds it hard to understand the full potential of 5G technology and how it can give them a competitive edge. Part of the problem is all the promises and the futuristic concepts that usually go with all the conversations about the 5G network. Even before there was a clear definition of 5G itself and the technology behind it.
“5G is more than just a generational step; it represents a fundamental transformation of the role that mobile technology plays in society. As demand for continuous connectivity grows, 5G is an opportunity to create an agile, purpose-built network tailored to the different needs of citizens and the economy.”
Mats Granryd | Director General | GSMA (Global System for Mobile Communications Association)
During the 2016 Mobile World Congress in Barcelona, the world’s largest exhibition for the mobile industry, I was visiting the Ericsson exhibition area, which occupied almost half of the hall. I was fascinated by all the demonstrations – there was a concept for a self-driving car, a demonstration on how drones can scan wind turbines for problems and thus prevent incidents, how small sensors can collect information for scientific research, and so on. Ericsson was showing so many different scenarios with great promises. But the technology for all of this was still absent.
And that’s why the business is so divided. A lot of promises, a lot of big investments, and still a future that is difficult to grasp, let alone measure. The situation reminds me of artificial intelligence (AI). Though its impact is growing, it’s still far away from the promises that were presented to the business.
And the thing is, that while we talk about how the big shift that 5G network will introduce in industries and society, the business is still thinking about the direct effect that it’ll have on its specific processes.

This leads us to the last myth or reality: There is no real business case for 5G because the investment looks unjustifiable and everything that is promised looks only like optimization of the processes and not revenue opportunities.
But the thing is that for a lot of businesses 5G looks like no brainer. If your clients will benefit from the immense increase in the speed and the lowest latency than 5G will give you new possibilities and can help you develop never-before-seen services. Not everything must be revolutionary, it just needs to have solid use cases and to deal with real clients’ pain points. An example is the partnership between Verizon and Corning that I mentioned before, or, for example, creating a VR and AR experience that can be used for training, creating a new streaming service, a lot better location services for the insurance business, and IoT devices that can save lives because they constantly send information. New things that we couldn’t even imagine become possible when we have a constant, super-fast connection that transfers a massive amount of data.
If your business won’t benefit from all of this, then you can wait for your 5G adoption. But think hard if there isn’t something that can give you a competitive edge.

Conclusion
5G network is not a myth. At least, not anymore. It is a disruptive technology that needs a lot of strategies, planning, and investments. It will be part of our future. That’s why the mindset “we will see what happens” and then we will catch up, is wrong. Even if the early adopters of the 5G network are moving slowly, when they gain traction, the race would already be lost for the others.
Support Ukraine against russian fascists! Defend Europe from horde! Glory to Ukraine! 🇺🇦

Head and Editor in Chief of EcmaScript2017 Journal. Senior JS Back-end Full stack developer and software architect.



Read Also
Why DevOps Managed Services Have Become More Popular and Important
M4uHD: Unveiling the Entertainment or Venturing into Uncertainty?
Smart Square HMH: Access, Features, Pros, Cons